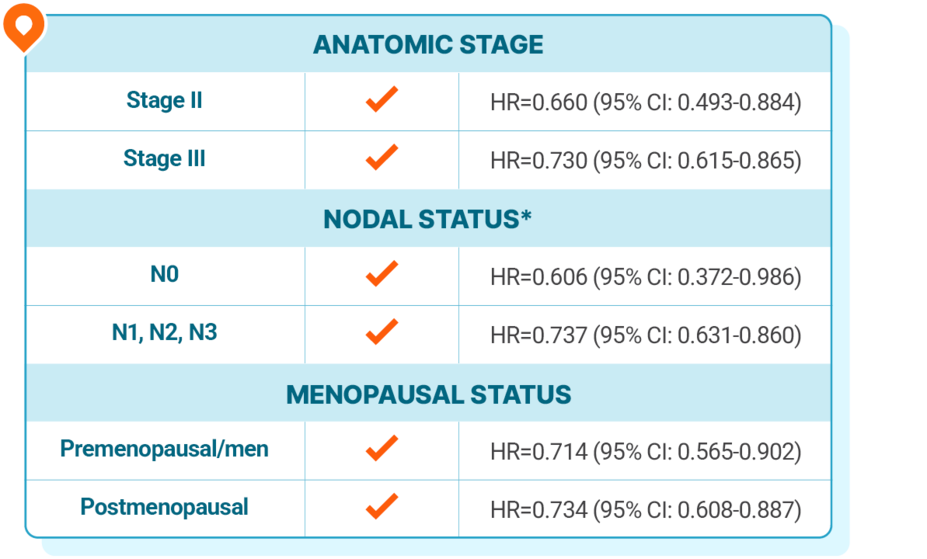
KISQALI + AI consistently improved iDFS across subgroups, regardless of stage, nodal status, or menopausal status
At 5 years, in patients with stage II/III HR+/HER2- eBC at high risk of recurrence,
iDFS results favored KISQALI across prespecified subgroups, including no nodal involvement
NATALEE: KISQALI + AI vs AI alone1
Hazard ratios reported as KISQALI + AI vs AI alone.
*Nodal status classification according to AJCC staging. Nodal status is from the worst stage derived per surgical specimen or at diagnosis.1
Results from the subgroup analysis included no prespecified statistical procedure controlling for type 1 error.
iDFS was defined as the time from randomization to the date of the first event of local invasive breast cancer recurrence, regional invasive recurrence, distant recurrence, contralateral invasive breast cancer, second primary non-breast invasive cancer (excluding basal and squamous cell carcinomas of the skin), or death (any cause).2
NATALEE was a randomized, multicenter, open-label, phase III study of KISQALI + letrozole or anastrozole (n=2549) vs letrozole or anastrozole (n=2552) for the adjuvant treatment of men and women with stage II/III HR+/HER2- eBC, including all those with node-positive or high-risk node-negative disease (eligible stages and nodal status include: anatomic stage group IIB-III, or anatomic stage group IIA that is either node positive, or node negative with histologic grade 3, or histologic grade 2 with Ki-67 ≥20% and/or high risk by gene signature testing). At a median follow-up of 33.3 months, with 509 iDFS (primary end point) events in the study (226 [8.9%] in the KISQALI arm and 283 [11.1%] in the NSAI-alone arm), iDFS at the 3-year landmark was 90.7% for KISQALI + NSAI vs 87.6% for NSAI alone (absolute difference 3.1%); there was a 25.1% relative reduction in the risk of an iDFS event; HR=0.749 (95% CI: 0.628-0.892).2-4

Meet your KISQALI patients
Identify eligible patients like Jasmine, Erin, and Katrice today