Reduced risk of recurrence
Do more today to help protect their tomorrow: KISQALI + AI can help prevent recurrence in the broadest population of patients with stage II/III HR+/HER2- eBC at high risk of recurrence.
In patients with stage II/III HR+/HER2- eBC,
Over 5 years, KISQALI delivered a 28% reduction in the risk of recurrence
The iDFS benefit deepened over time with KISQALI + AI, beyond the 3-year treatment period
In the 3-year final analysis (median follow-up of 33.3 months)1,2:
iDFS at 3 years was 90.7% for KISQALI + AI vs 87.6% for AI alone (absolute difference 3.1%)
There was a 25.1% relative reduction in the risk of an iDFS event; HR=0.749 (95% CI: 0.628-0.892)
In an interim analysis, at a median follow-up of 28 months, a statistically significant reduction in risk was achieved despite the greater challenge of showing clinical benefit in a broad range of patients.1,3,4
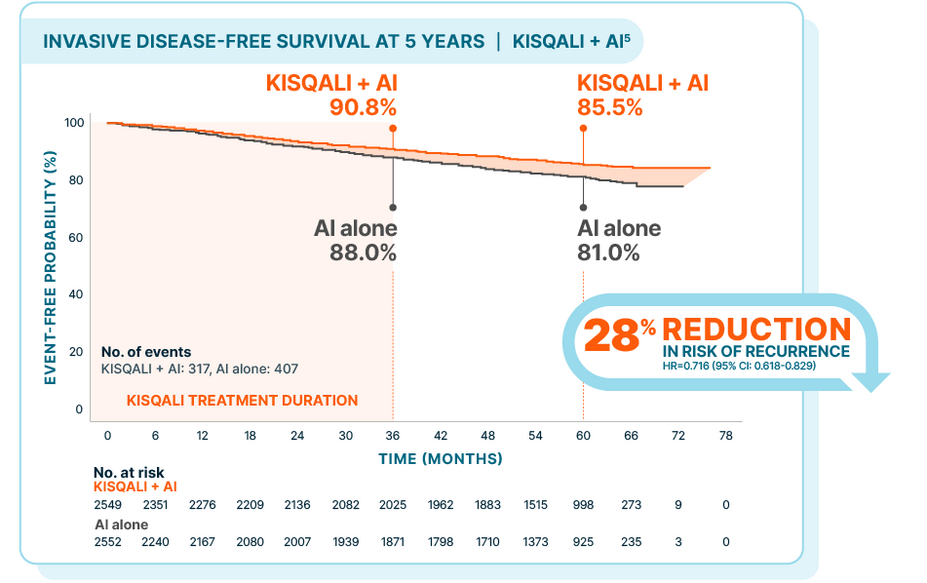
NATALEE: KISQALI + AI vs AI alone
At a median follow-up of 55.4 months
Hazard ratio is based on stratified Cox model.6
iDFS was defined as the time from randomization to the date of the first event of local invasive breast cancer recurrence, regional invasive recurrence, distant recurrence, contralateral invasive breast cancer, second primary non-breast invasive cancer (excluding basal and squamous cell carcinomas of the skin), or death (any cause).1
In the 5-year prespecified analysis5:
At 3 years: 2.7% absolute difference*
At 5 years: 4.5% absolute difference
At the time of data cutoff, only 12.4% of patients receiving KISQALI + AI had experienced an iDFS event vs 15.9% of patients treated with AI alone
The 5-year analysis was prespecified and observational in nature; as such, there was no prespecified statistical procedure controlling for type 1 error
*The difference between percentages does not equal 2.7 due to rounding.5
NATALEE was a randomized, multicenter, open-label, phase III study of KISQALI + letrozole or anastrozole (n=2549) vs letrozole or anastrozole (n=2552) for the adjuvant treatment of men and women with stage II/III HR+/HER2- eBC, including all those with node-positive or high-risk node-negative disease (eligible stages and nodal status include: anatomic stage group IIB-III, or anatomic stage group IIA that is either node positive, or node negative with histologic grade 3, or histologic grade 2 with Ki-67 ≥20% and/or high risk by gene signature testing). iDFS was the primary end point.1,2
AI, aromatase inhibitor; eBC, early breast cancer; HER2-, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative; HR, hazard ratio; HR+, hormone receptor-positive; iDFS, invasive disease-free survival.
KISQALI + AI consistently improved iDFS across subgroups, regardless of stage, nodal status, or menopausal status
KISQALI may be right for a variety of patients with stage II/III HR+/HER2- eBC.

Meet your KISQALI patients
Identify eligible patients like Jasmine, Erin, and Katrice today